ngrok
To access a host using SSH, if you are on the same local network as the host or if the host has a public IP, you can connect directly using the SSH command with the host’s IP address. However, most companies and homes use local networks and cannot assign a public IP to each host within the network. In such cases, network tunneling is needed to connect to hosts within a local network from the outside.
ngrok is a reverse proxy tool that can expose a local network’s port to the public internet. By using ngrok, you can also expose the port used by SSH, thereby achieving SSH tunneling through the local network.
Register and Download ngrok
Visit https://ngrok.com/ to register for an ngrok account and download the ngrok client.
Retrieve ngrok Token
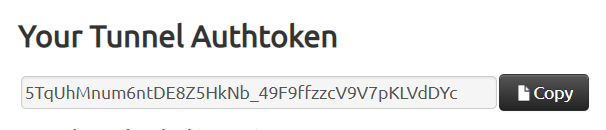
Visit https://dashboard.ngrok.com/auth to view and copy your token.
Start ngrok on the Local Network Machine
Connect your ngrok account:
ngrok authtoken 5TqUhMnum6ntDE8Z5HkNb_49F9ffzzcV9V7pKLVdDYc
Start ngrok and open port 22 for forwarding:
ngrok tcp 22 --log=stdout > "$HOME/ngrok.log" --region ap &
Here, the region parameter ap represents the Singapore node of ngrok, which offers faster access compared to the US node. Visit https://ngrok.com/docs#config-options to see all supported regions.
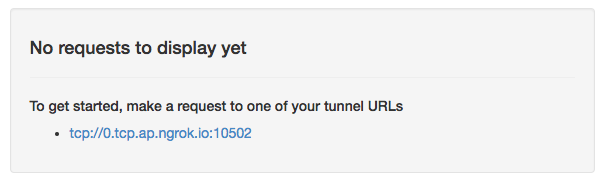
Access http://127.0.0.1:4040.
You will see an address starting with tcp. By accessing this address, you can forward to the local machine’s port 22.
Access the Local Network Machine via SSH
Once you have the forwarding address, you can access the local network machine from the internet using the SSH command. Based on the example above, the SSH access command is:
ssh -p 10502 [email protected]
Important Considerations
Since all traffic must pass through ngrok’s servers, and ngrok’s service nodes are only in locations like the US and Singapore, the speed can be relatively slow. Additionally, if there are security vulnerabilities in ngrok’s service nodes, there is a potential risk of sensitive information leakage.