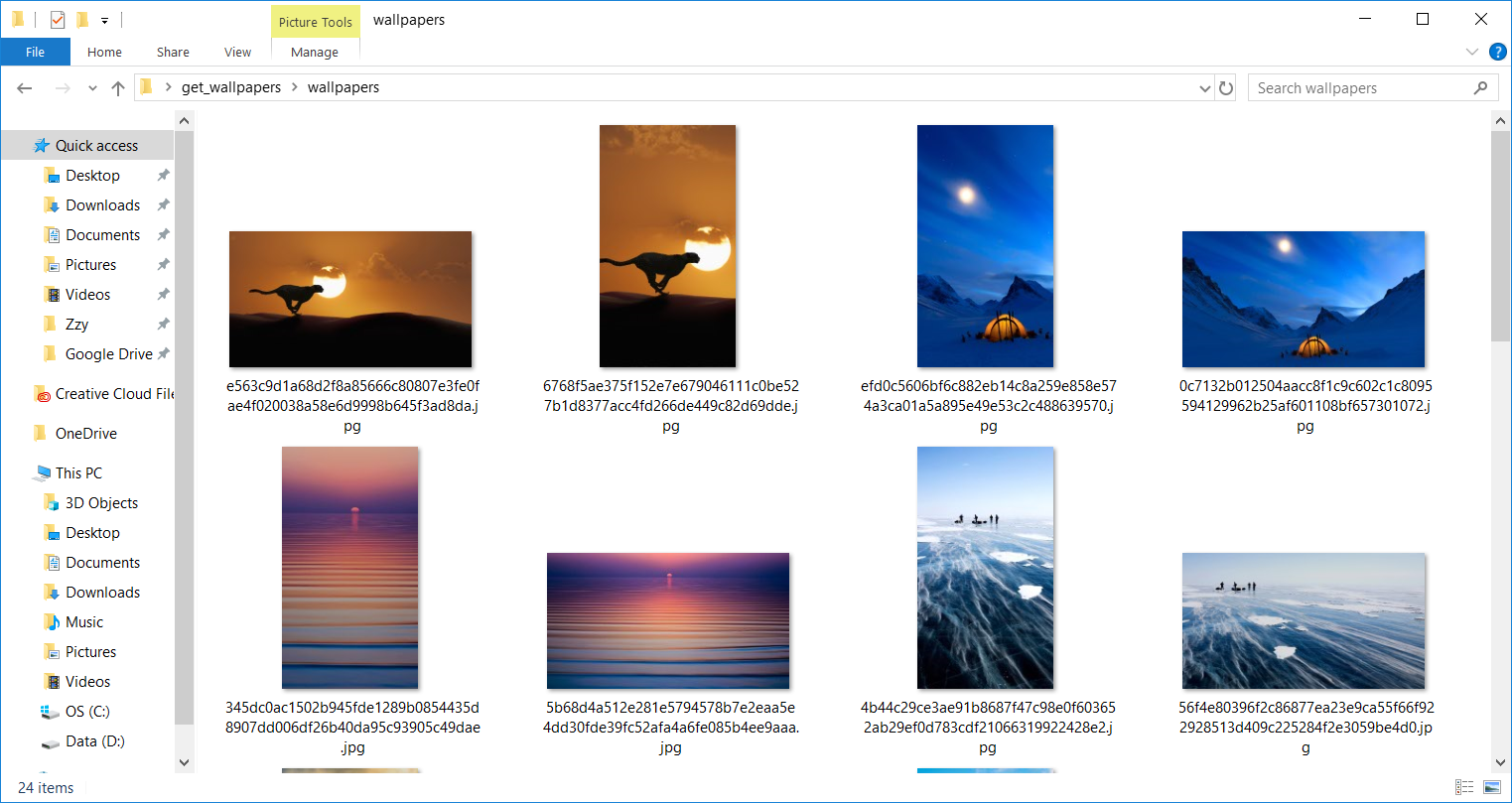
Windows 10 users might notice that every time they boot up, the lock screen displays a different beautiful image. These images are often selected from outstanding photography works and are quite exquisite.
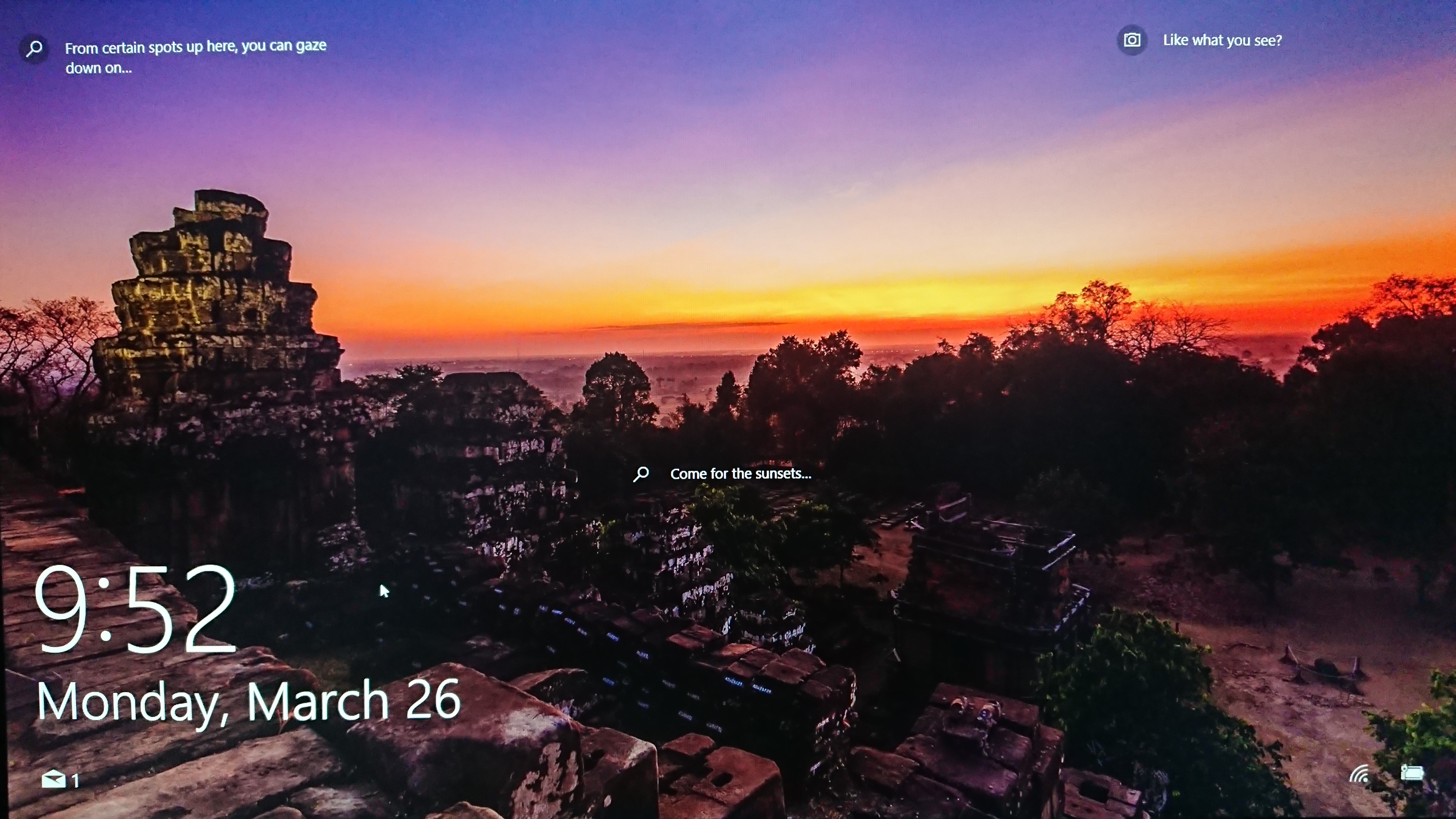
However, since the system automatically changes these images, even the most beautiful ones might be replaced the next time you start your computer.
With the help of Python, we can use a few simple lines of code to batch extract these beautiful lock screen images. By setting your favorite images as desktop backgrounds, you no longer have to worry about them being replaced.
Extraction Principle
The Win10 system automatically downloads the latest lock screen wallpapers and stores them in a system folder located at C:\Users\[Username]\AppData\Local\Packages\Microsoft.Windows.ContentDeliveryManager_cw5n1h2txyewy\LocalState\Assets
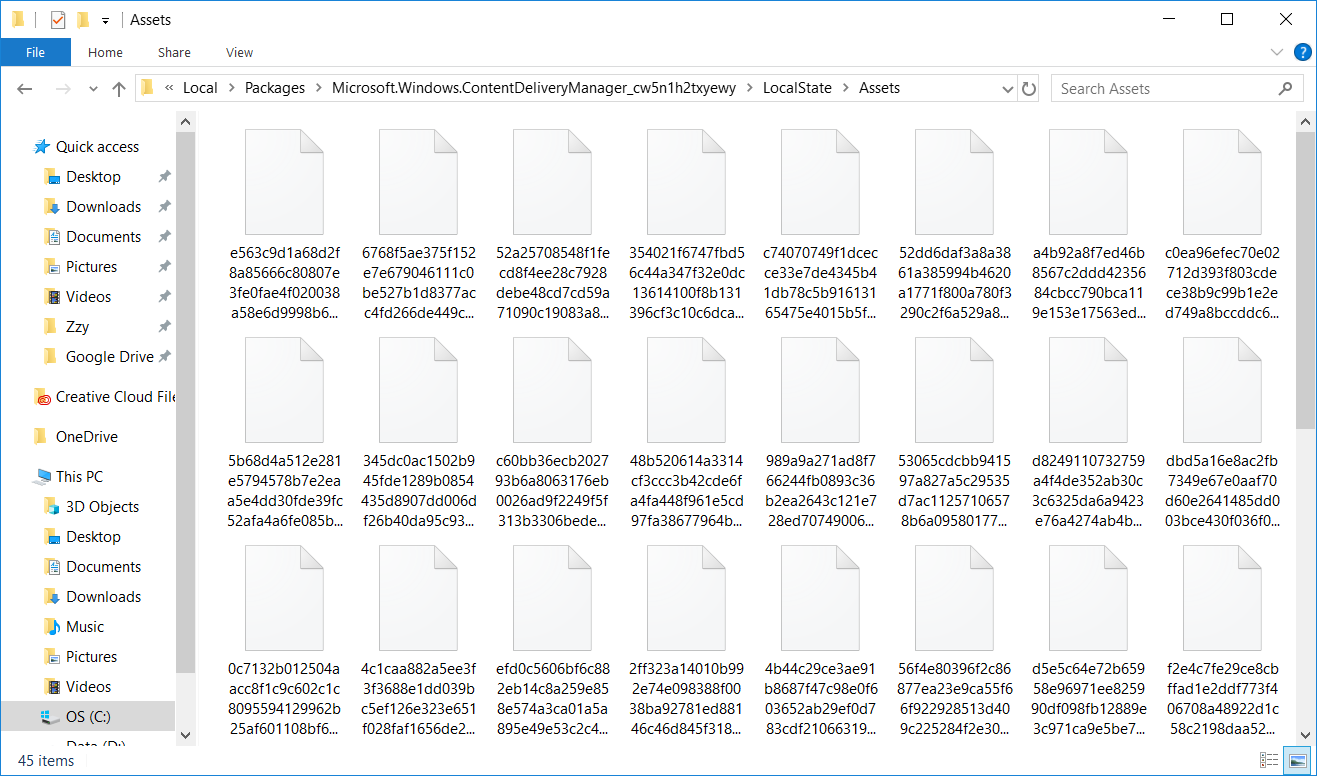
Opening this folder directly, you will find multiple randomly named files, each representing an image. However, since these files lack extensions, they cannot be previewed. To avoid damaging system files and to convert these files into a previewable format, we use Python to copy these files and add JPG as their extension.
Implementation Code
import os, shutil
from datetime import datetime
# Use the wallpapers folder in the directory where this file is located as the directory to save images
save_folder = dir_path = os.path.dirname(
os.path.realpath(__file__)) + '\wallpapers'
# Dynamically get the location where the system stores lock screen images
wallpaper_folder = os.getenv('LOCALAPPDATA') + (
'\Packages\Microsoft.Windows.ContentDeliveryManager_cw5n1h2txyewy'
'\LocalState\Assets')
# List all files
wallpapers = os.listdir(wallpaper_folder)
for wallpaper in wallpapers:
wallpaper_path = os.path.join(wallpaper_folder, wallpaper)
# Files smaller than 150kb are not lock screen images
if (os.path.getsize(wallpaper_path) / 1024) < 150:
continue
wallpaper_name = wallpaper + '.jpg'
save_path = os.path.join(save_folder, wallpaper_name)
shutil.copyfile(wallpaper_path, save_path)
print('Save wallpaper ' + save_path)
First, determine the folder location where the system stores lock screen images. Since the folder is located within the user’s personal folder and each user’s username is different, we need to dynamically obtain the path through the system’s LOCALAPPDATA variable. The code will save the extracted images in the wallpapers folder, so if there is no wallpapers folder in the directory where the code file is located, you need to manually create one.
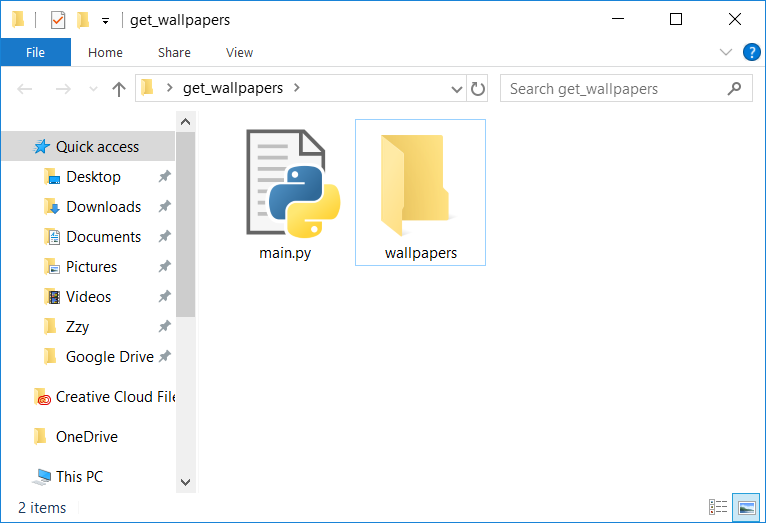
Run the above Python code, and then open the wallpapers folder to see the extracted lock screen images.